Module 3.1
Bipolar Junction Transistors
- Section 3.1 Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTs).
- • BJT circuit symbols.
- • BJT output transistors.
- • Complementary pairs.
- • Small signal BJTs.
- • Common transistor packages.
- Section 3.2 Making Transistors.
- • Germanium Alloy Diffused Transistors.
- • Silicon Planar Transistors.
- Section 3.3 How a BJT Works.
- • Doping.
- • Current Flow.
- Section 3.4 BJT Animation.
- • Base bias
- • Collector current
- • Junction potential
- Section 3.5 Current Gain.
- • Bipolar Transistor Characteristics
- • Transfer.
- • Input.
- • Output.
- • Mutual.
- Section 3.6 Transistor Connections.
- • Common Emitter.
- • Common Collector.
- • Common Base.
- Section 3.7 Bipolar Transistor Quiz.
- • Check your understanding of Bipolar Transistors.
What are BJTs?
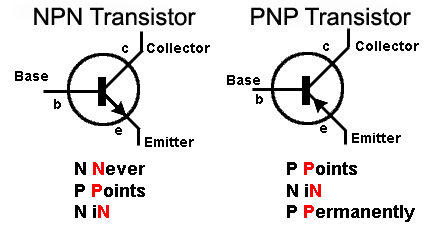
Fig. 3.1.1 Bipolar Junction Transistors
Bi-polar transistors are amongst the most widely used devices for amplification of all types of electrical signals in discrete circuits, i.e. circuits made from individual components rather than integrated circuits (I/Cs). BJTs are also used in circuits together with I/Cs , since it is often more practical to use discrete output transistors where a higher power output is needed than the I/C can provide. For example an integrated circuit may carry out all of the processing of the signals in a system, but then pass the processed signal to a single discrete transistor or a pair of matched transistors for power amplification to drive a loudspeaker or other output device. It is also often more convenient to use a discrete transistor for an individual circuit within a larger system, for which I/Cs are not readily available.
Transistors come in many shapes and types. A selection of typical bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) is shown in Fig 3.1.2
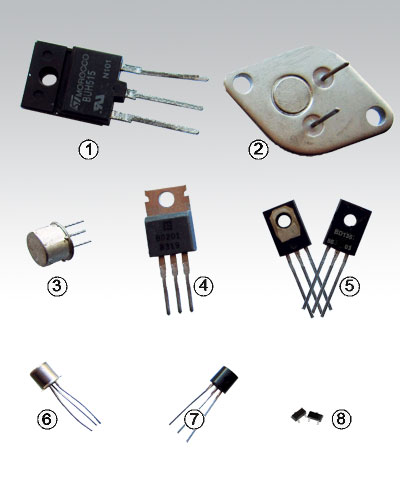
Fig. 3.1.2 Typical Bipolar Junction Transistors
-
1. BUH515
High Voltage (1500V) high power (50W) NPN fast switching transistor in an ISOWATT218 package, originally designed for use in analogue TV timebases but also used in switched mode power supplies. 2. 2N3055
NPN Silicon Power transistor (115W) designed for switching and amplifier applications. Can be used as one half of a complementary push-pull output pair with the PNP MJ2955 transistor.3. 2N2219
NPN silicon transistor in a metal cased TO-39 package, designed for use as a high speed switch or for amplification at frequencies from DC (0Hz) up to UHF at about 500MHz.4. 2N6487
General purpose NPN output transistor with a power rating up to 75W in a TO-220 package.5. BD135/BD136
Complementary (NPN/PNP) pair of low-medium power audio output transistors in a SOT-32 package.6, 7 and 8. 2N222
Small signal general purpose amplifier and switching transistors like the 2N2222 and 2N3904 are commonly available in a variety of package types such as the TO-18 metal cased package (6), and the cheaper plastic TO-92 version (7) for through-hole mounting on printed circuit boards, as well as in surface mount SOT-23 versions (8).
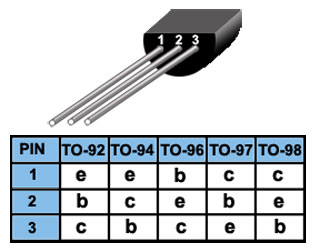
Fig. 3.1.3 TO-92 package variations
Many transistor package types are also available with alternative connection layouts. The TO-92 package for example has variants TO-94, TO-96, TO-97 and TO-98 all with similar physical appearance, but each with a different pin configuration. Where different package variants are available, these are usually identified on the data sheet for each particular transistor type. Typical variations, such as those for the TO-92 to 98 series of packages used for transistors such as the 2N2222 are illustrated in Fig. 3.1.3.


